Research Introduction
Our lab provides simulation studies for material sciences,
which is useful for industrial applications.
Our viewpoint of the studies is physical chemistry of
molecular ensembles in interfaces.
Properties of materials are governed by
the bulk and the surface properties.
The properties of the materials are
strongly affected by the molecular properties of interface,
which is described as
"God made the bulk; surfaces were invented by the
devil" by Wolfgang Pauli.
In other words, we are able to design innovative
properties of materials controlling by the interfaces.
For example, our bodies are made of ionic polymers
(polyelecrolytes solution) and
transformation of materials and energy in
high quality as the living systems are
realized by controlling long-range Coulomb interactions
between molecules in solution.
For industrial purpose,
the characteristics of the interfaces are important in
lubrication or in electrodes in batteries.
In materials simulation, there are two level of
simulation, quantum level and the level of atom ensemble.
The latter is named molecular simulation in a narrow sense,
and we are involved in the latter ones.
Although the molecular simulations seems rather easy
than quantum simulations
because they say they solve Classical Newtonian equation
of motions,
molecular simulations are based on complex
statistical mechanical basis and
have connection with fluid dynamics,
and development of simulation methods
are not finished yet.
The development of new simulation method
such as multiscale, mutli-physics scheme
in electron, atom and fluid level
is also our object of researches.
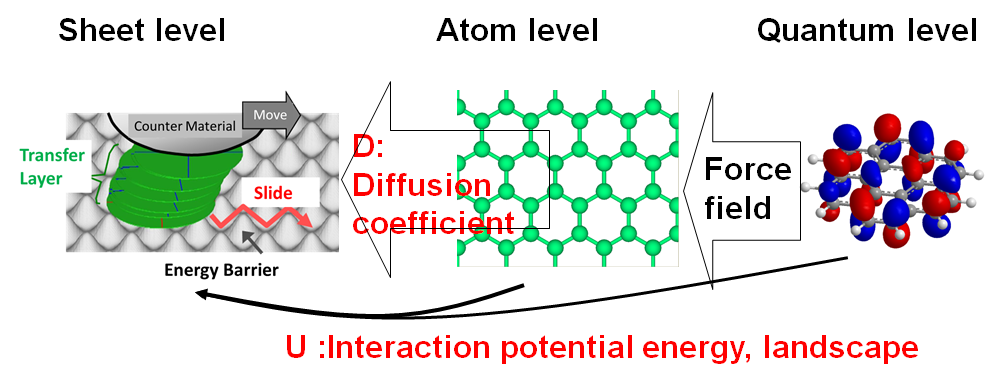
Algorithms for molecular simulations
The major simulation results from our laboratory are calculated by self-developed softwares.Molecular Dynamics
We have developed non-equilibrium molecular dynamics simulator which can simulate dynamics of organic molecules, waters, metals, ionic solids, covalent bonded amorphous materials and so on. The simulator is MPI parallelized and tested in the next generation super computer project. It is also expanded to calculate under special condition such as shear condition, high pressure and unique ensemble in statistical mechanics.Monte Carlo Brownian Dynamics
Metropolis Monte Carlo method is famous as a method to calculate partition functions under equlibrium condition. We have shown Metropolis Monte Carlo method would be a numerical calculation method of Fokker-Planck equation, and solve the Brownian motion of colloidal suspensions. We adopted the method to diffusion motions of ions in liquids, segment motions of polymer solutions and sliding motion of graphene sheets.
Simulation of ion flows in nano interfaces
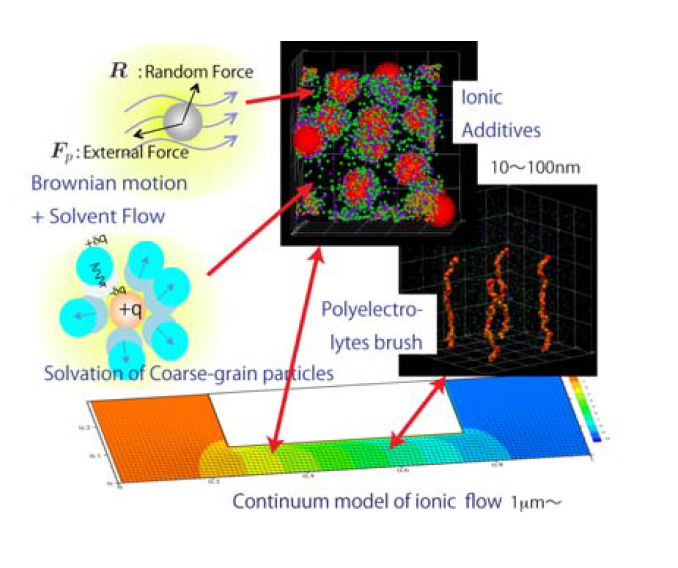
Coulomb interaction is the most strong and long-ranged force
among the intermolecular forces.
Batteries are the typical devices using the interaction and
highly controlled complex systems such as bio-system
utilize the force.
Ionic solutions has, however, microscopic features such as
solvation, coarse-grained method to treat these
features is under development.
We are planning to make molecular simulator, which can
simulate molecular dynamics to continuum flow dynamics
including solvation effect, hydrodynamic interaction
of solvents around ions.
We adopt these methods to the low friction of polyelectrolyte
brushes to Sodium ion secondary battery systems.
Tribology
Tribology is "the science and technology of interacting surfaces in relative motion" first supposed by Prof. Jost in 1966. Tribology is one of the most important themes of our laboratory. We study friction, lubrication, wear in molecular level using computer simulations.
Elasto-hydrodynamics Lubrication
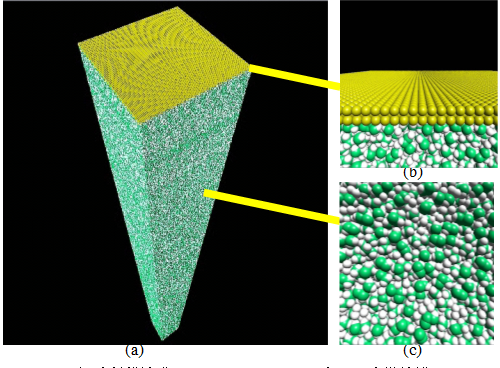 Tribo-molecular dynamics simulation is the simulation
method developed in 1990s to simulate properties of oils.
Molecular modeling of base oil molecules is suitable
applicants for the application. For this purpose, non-
equilibrium all-atom molecular dynamics simulations
of the traction properties of hydrocarbon fluids under
elastohydrodynamics lubrication were studied.
Traction fluids are used in continuous
variable transmissions in order to transmit forces be-
tween two steel rollers, and the traction properties
significantly depend on the structure of the fluid mole-
cules. The effects of the oil film thickness, shear
rate and pressure were investigated using super
parallel computer in national project. The dynamic
mechanisms of the momentum transfer on layers of
fluid molecules were also analyzed by focusing on the
intermolecular interactions and intramolecular
interactions.
Recently,
the non-slip boundary condition
assumed in continuum lubrication theories was
confirmed on a molecular level
by huge molecular dynamics
simulation of oils.
Tribo-molecular dynamics simulation is the simulation
method developed in 1990s to simulate properties of oils.
Molecular modeling of base oil molecules is suitable
applicants for the application. For this purpose, non-
equilibrium all-atom molecular dynamics simulations
of the traction properties of hydrocarbon fluids under
elastohydrodynamics lubrication were studied.
Traction fluids are used in continuous
variable transmissions in order to transmit forces be-
tween two steel rollers, and the traction properties
significantly depend on the structure of the fluid mole-
cules. The effects of the oil film thickness, shear
rate and pressure were investigated using super
parallel computer in national project. The dynamic
mechanisms of the momentum transfer on layers of
fluid molecules were also analyzed by focusing on the
intermolecular interactions and intramolecular
interactions.
Recently,
the non-slip boundary condition
assumed in continuum lubrication theories was
confirmed on a molecular level
by huge molecular dynamics
simulation of oils.
Boundary Lubrication
Boundary lubrication is the phenomena that a few molecular layers cover the solid surface in order to protect surface and minimize friction. We used molecular dynamics to solve the dynamics of organic monolayers, and water layers. We also show that the low friction mechanism of DLC-Si (silicon contained diamond like carbon) coating is due to the boundary film of water molecules bounded by hydrogen bonds between SiOH (silanol) site on the surface and water molecules.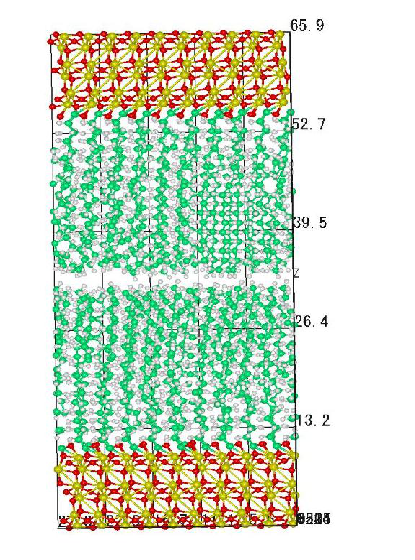
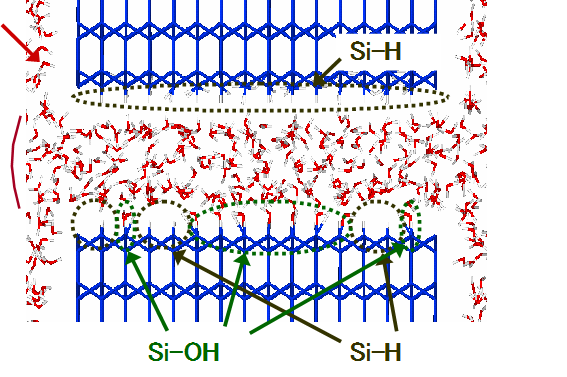
Solid Lubrication
Mechanism of super low friction of layered materials was long standing question. We made coarse-grained molecular simulator to simulate sliding motion of transfer layer of graphene and found low friction mechanism named thermal escape motion. The origin of solid friction in crystals is also investigated. Semi-infinite atom vibration model of solids using Green fnuction is introduced and we found the low frequency phonon dissipation is related to the origin of solid friction.
Next Generation Batteries
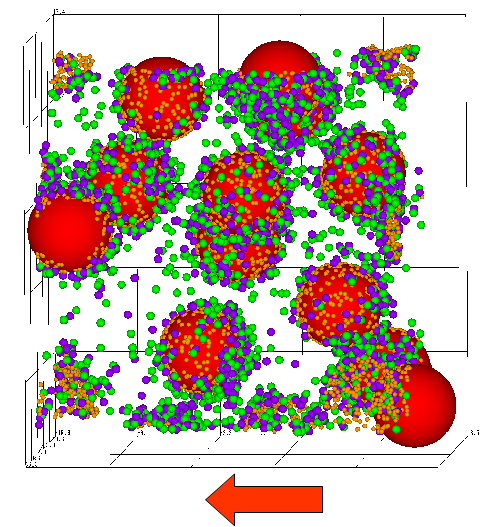
80 % of Lithium in the world is produced in Chile. From the point of view of element strategy, development of sodium secondary batteries is expected. The properties of electrolyes solution for secondary batteries and binder polymer for the negative electrode are studied in our laboratory using multi-scale ion flow simulator. The improvement of ion transport effect of additives for the electrolyte solution, structure and dynamics of polymer binders for the negative electrodes are the topics.
Plyelectrolytes Solutions, Bio-molecular systems
Polyelectrolyte solution governed by long-range
Coulomb interaction is the soft and intelligent
system which is found in living cells.
On the other hand, due to the complexity, which has
its origin of soft nature and
multi-scaled and long-range correlations
it is most difficult system to treat by
molecular simulation.
We developed a simulator from 1990s to treat
polyelectrolyte solutions adequately and
shown the static and dynamic nature of ion atmosphere around
biopolymers, such as DNA and polyelectrolyte brushes
which is model of synovial joints.
Recently we are focusing on the thermodynamic role of
water solvents.
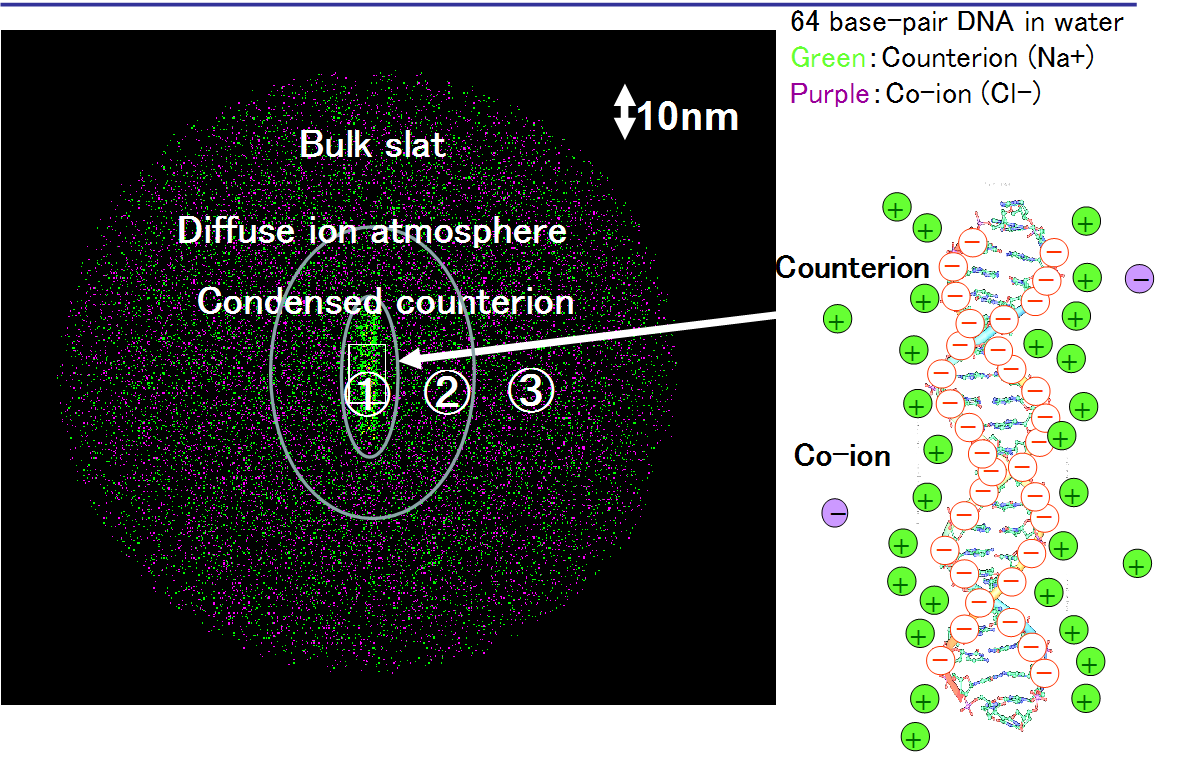
Counterion condensation on surfaces
is essential theme of our research.
We found counterion condensation occur in
rod-like polyions, charged spheres, confined planes,
brushes and nano-pores
as far as the dynamical change.



Simulation of automotive transportations
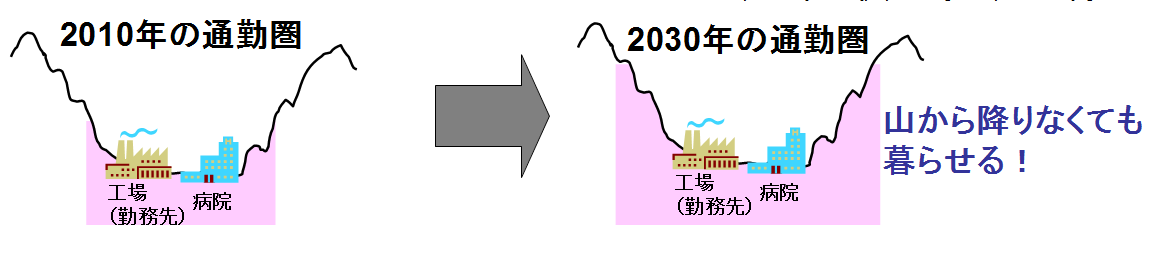
A feature of our graduate school is to create an academic field of simulation studies including social, human and nature. We would like to propose simulation studies, which solve social problems by industrial revolution. In Japan, depopulation and population ageing at the countryside are serious social problems. Sometime, intensification of the social resources is said to be the answer of this problem. However, intensification means shrinkage of the "populatable zone" where our ancients made effort for cultivation. Here we simulate the ability of low efficiency and auto driving vehicle to make wider commutable area in countryside. Hyogo prefecture is called "miniature of Japan" because there are mega cities, islands, mountains and plains. Therefore Hyogo is good place to make our case studies.
